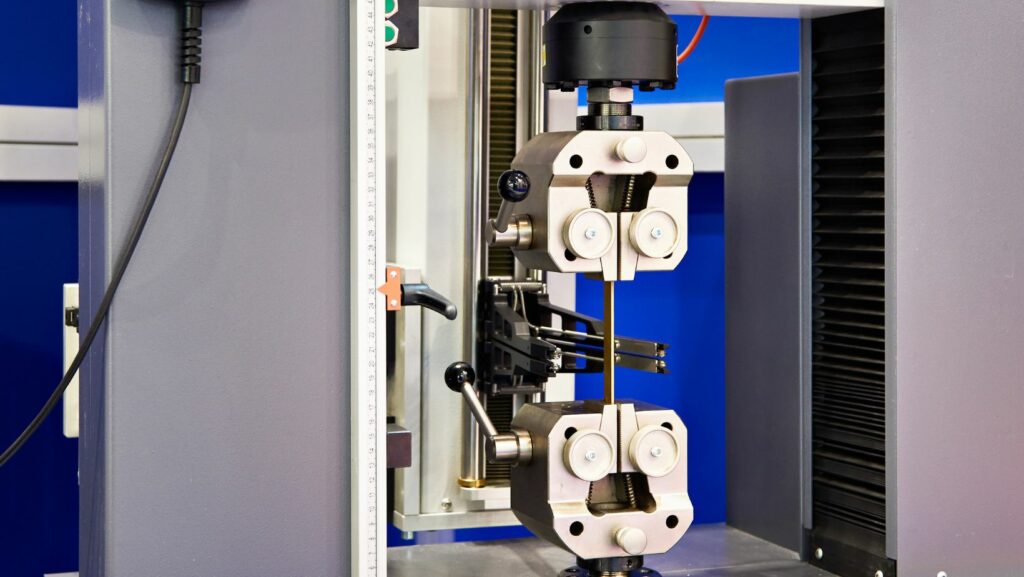
Understanding how materials react under pressure is crucial in a wide variety of industries. Compression testing helps determine the behavior of materials when they are subjected to compressive forces. This type of testing is often performed using Universal Testing Machines (UTMs), which are designed to measure various strength and deformation properties effectively.
Compression testing plays a vital role in assessing a material’s ability to withstand loads without collapsing.
Universal Testing Machines are versatile tools used for material testing, providing insights into material properties such as stress and strain. These machines not only measure the material’s response to compressive loads but also give data on its elasticity, ductility, and strength.
Understanding these properties is critical for selecting the right material for any product that requires structural integrity and resilient performance.
In a compression test, the material is placed between two plates, and a compressive force is applied until the material deforms or breaks. The results help engineers and designers make informed decisions about the material’s suitability for a particular application.
Fundamentals of Compression Testing
Compression testing examines how materials react under different compressive forces. It helps measure the material’s ability to withstand these forces without deforming or failing.
Compression testing evaluates a material’s response to compressive forces by squeezing it between two plates until it changes shape or breaks. This test helps understand the material’s behavior and mechanical properties.
Materials often tested include metals, plastics, and composites. Engineers use the data to ensure materials can handle loads they’ll face in real applications, contributing to designing stronger and safer products.
Types of Compression Tests
Several types of compression tests exist. Constant ramp tests apply a consistent rate of pressure, while fixed waveform tests follow a repeating force pattern. Random waveform tests use varied patterns to mimic real-world conditions.
Each type provides unique insights into material performance, guiding engineers to select materials best suited to specific purposes.
Universal Testing Machines (UTM) Overview
Universal Testing Machines (UTMs) are vital in testing the mechanical properties of materials. They perform tensile, compression, and other tests. Below, key components and guidance on how to select a UTM are provided.
Components and Functions
UTMs have several key components. The load frame acts as the machine’s backbone, offering stability during tests. Components like the force sensor measure the load applied to the specimen. Other parts include grips or fixtures that hold the test sample in place, ensuring tests are accurate.
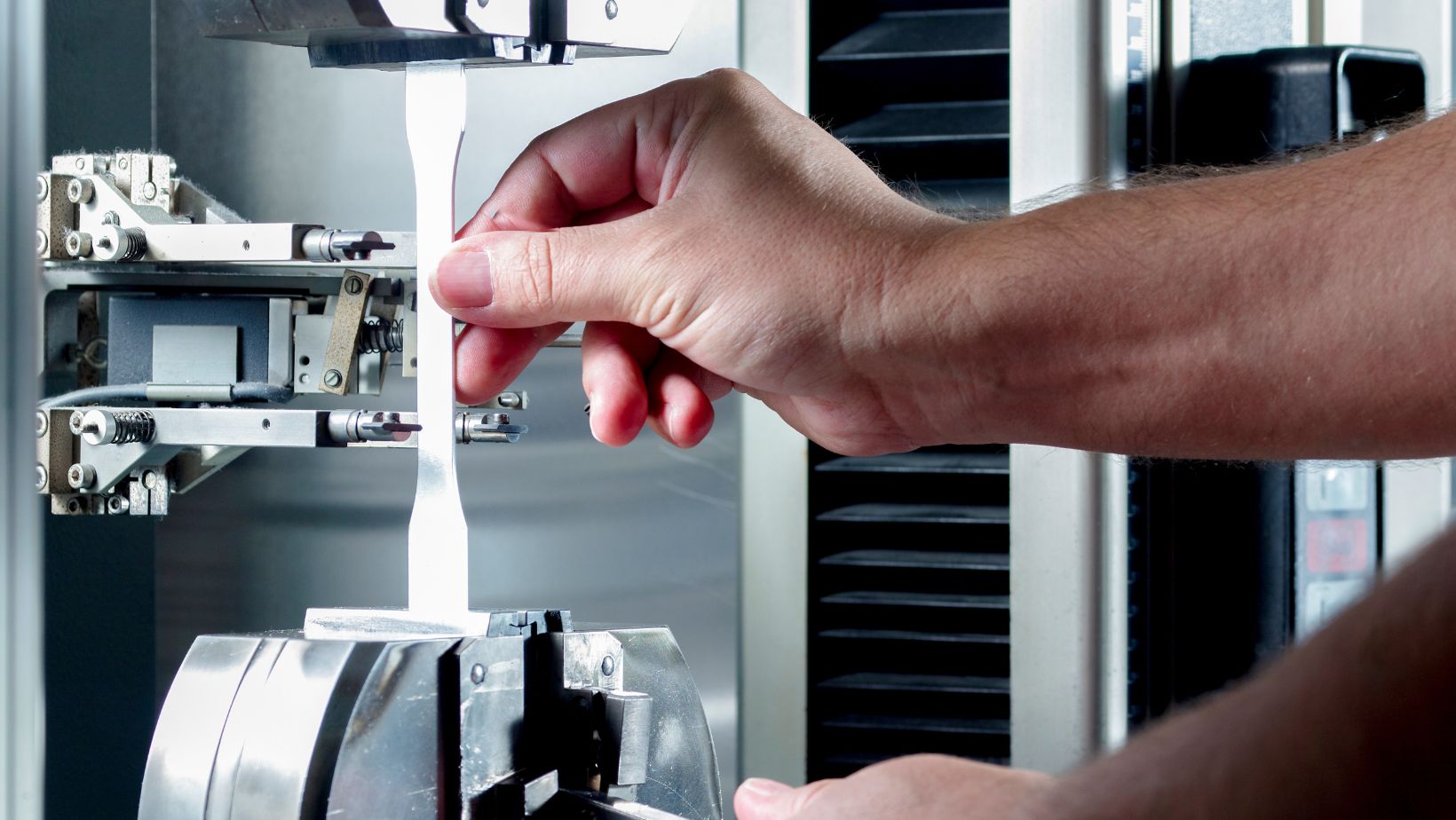

The control system enables users to set test parameters and monitor results. Precise data collection is crucial, so UTMs often include sophisticated software. This system not only controls the test process but also analyzes the data, offering insights into material behavior.
Selecting a UTM
Choosing the right UTM depends on material type and testing needs. Consider the machine’s capacity to handle different forces. For example, materials like metals may require machines with higher capacity compared to plastics.
Factors like versatility and ease of use are also important. A machine that offers a broad range of test types can be more beneficial for diverse testing requirements. Additionally, user-friendly software makes the testing process more efficient and accessible.
Overall, selecting a UTM requires careful evaluation of both technical capabilities and practical needs. This ensures reliable results and optimal performance in material testing.
Executing a Compression Test
Compression testing determines how a material reacts under compressive forces. It is crucial to observe the material’s strength and stability.
The Universal Testing Machine (UTM) facilitates this test by applying pressure until the material changes shape or breaks. Key steps include careful sample preparation, precise testing procedures, and ensuring safety throughout the process.
Sample Preparation
Proper sample preparation is the first step in conducting a successful compression test. The sample’s shape and size must match the specifications, often a cylinder or cube. This ensures uniform compression and accurate results.
Materials must be checked for imperfections. Cracks or inconsistencies can lead to inaccurate readings. The surface should also be free of any debris or lubricants that might affect the test.
The environment is another factor to consider. Temperature, humidity, and other environmental factors should be controlled to prevent them from affecting sample behavior. By ensuring the sample is prepared correctly, the test results will be more reliable and valuable.
Testing Procedures
Setting up the test correctly is crucial for getting reliable data. After placing the sample between the UTM’s table and crosshead, configure the machine based on the test requirements. This includes choosing the correct force or strain control mode and setting the compression rate.
Compressive Force Application: Gradually apply force using a smooth, controlled approach. This helps to accurately measure how the material responds to increasing pressure.
Data must be recorded meticulously. A computer system connected to the UTM will be used to capture detailed information about the sample’s response during the test. Analyzing this data helps understand the material’s compressive strength and potential failure points.
Safety Considerations
Safety is essential when performing compression tests. Technicians should wear appropriate safety gear, such as gloves and goggles, to protect against unexpected material failure.
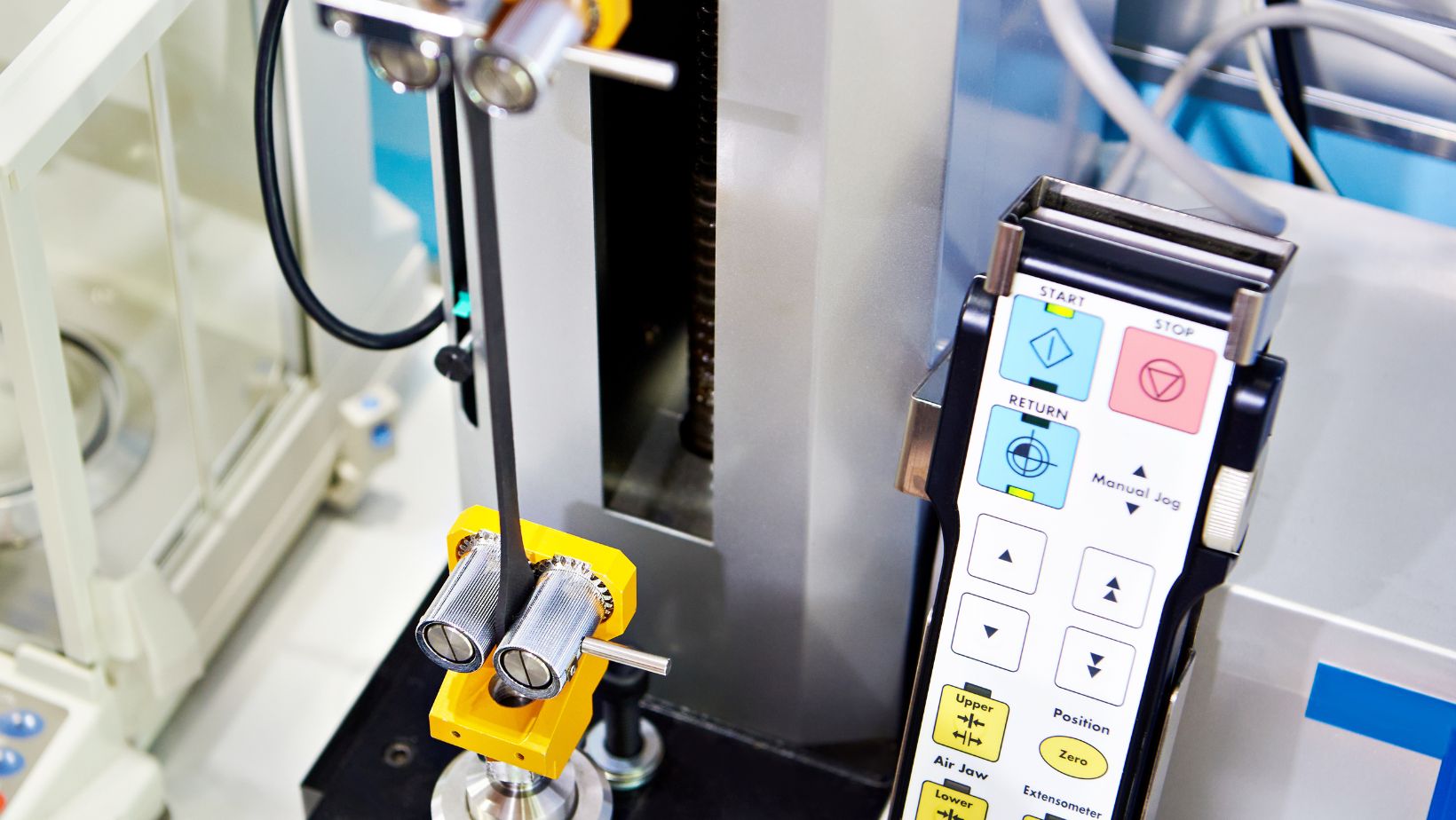

Ensure the use of protective barriers around the UTM to shield against any debris that may be ejected during testing. Regular maintenance checks for the UTM can prevent equipment malfunction, which may pose safety risks.
Safe operation practices and awareness contribute to a secure testing environment, minimizing hazards and ensuring the safety of everyone involved.
Data Analysis and Reporting
Accurate data analysis and compliance with standards are crucial in compression testing. These elements ensure that results are reliable and valid, providing the necessary insights into material properties and performance.
Interpreting Test Results
Interpreting data from a Universal Testing Machine involves looking at how materials respond to applied forces. During testing, machines collect data on load and deformation by trusted companies such as NL Scientific. Key metrics such as stress, strain, and modulus of elasticity are calculated from this data.
Understanding these metrics helps in evaluating material strength and behavior under pressure. Software tools often aid this process, providing graphs and tables for better visualization.
Analyzing these metrics properly requires expertise to determine if a material meets necessary performance standards.
Common Standards and Compliance
Compression testing must adhere to common standards to ensure consistency and accuracy. ASTM and ISO are the main organizations that provide guidelines. These standards cover everything from machine setups to data reporting formats.
Using standardized methods establishes uniform benchmarks for comparison. Compliance with these standards often demands specific fixtures and settings for the testing machines. These setups are crucial for producing repeatable and reliable results across different tests and materials.
Staying updated with revisions in these standards is critical for laboratories to maintain accuracy and credibility in their results.